Choosing the right light bulb can feel like navigating a labyrinth—one wrong turn and you’re left in the dark! But don’t worry; I’m here to light your path!
MR8, MR11, MR16, GU4, GU5.3, and GU10 bulbs differ mainly in size, base type, voltage requirements, and beam angle. MR bulbs feature a multifaceted reflector for focused lighting, while GU bulbs vary in pin base sizes for different fixtures.
Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision when selecting or replacing bulbs. In this guide, we’ll delve deeper into the specifics of each type and explore their best use cases to help you choose the perfect bulb.
MR16 bulbs use a multifaceted reflector for focused lighting.真
MR16 bulbs are designed with a multifaceted reflector to concentrate light into a narrow beam, ideal for spotlighting.
How Do Base Types Affect Bulb Compatibility?
Understanding bulb base types is essential for ensuring compatibility with your lighting fixtures.
Bulb base types, such as GU4, GU5.3, and GU10, determine compatibility with fixtures by defining the pin size and configuration. Incorrect base types can lead to improper fitting and electrical issues, making it crucial to match the base type with the fixture requirements.
The Importance of Pin Base Sizes
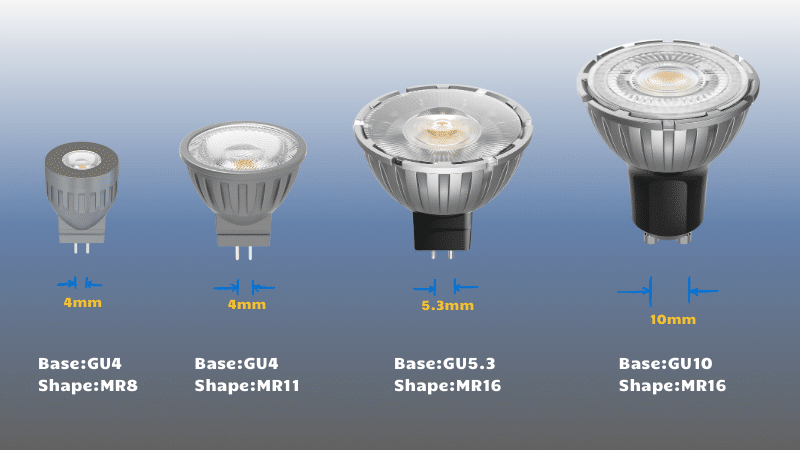
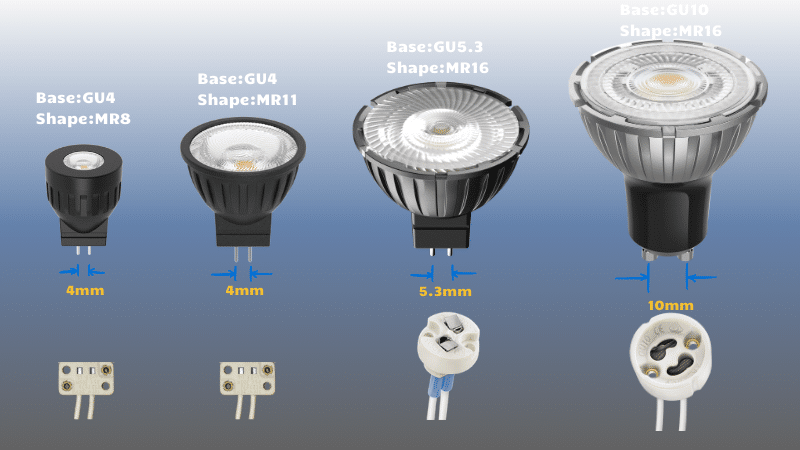
Base types significantly impact a bulb’s compatibility with a fixture, primarily through the pin base size. For example, GU4, GU5.3, and GU10 bases each have specific diameters and pin spacing that fit corresponding sockets. Using the wrong base type can prevent a bulb from fitting securely or even powering on.
- GU4: Typically used in low-voltage applications, this base has a pin spacing of 4mm, suitable for compact fixtures.
- GU5.3: With a 5.3mm pin spacing, this base is often found in spotlights and downlights requiring more power.
- GU10: Unlike the previous bases, GU10 uses a twist-and-lock mechanism, commonly seen in mains voltage applications.
It’s important to check your fixture’s specifications before purchasing bulbs to ensure they have the correct pin base size1.
Voltage Compatibility
Voltage compatibility is another critical factor related to base types. Different bases may signify different voltage requirements, affecting the bulb’s performance and safety.
- Low Voltage: Bases like GU4 and GU5.3 typically operate at 12V, requiring a transformer in some fixtures.
- Mains Voltage: GU10 bulbs operate directly at 120V or 240V depending on your location, eliminating the need for a transformer.
Matching the voltage requirements with your electrical system is essential to avoid potential hazards.
Influence on Design and Aesthetics
The choice of base type can also impact the design and aesthetics of your lighting setup. MR bulbs with multifaceted reflectors offer focused beams suitable for accent lighting. Meanwhile, GU bulbs provide a broader range of light distribution options based on their pin configuration and base type.
Knowing how different bulb designs2 and base types work together can help in creating desired lighting effects in your space.
GU10 bulbs require a transformer for operation.偽
GU10 bulbs operate at mains voltage (120V/240V) without a transformer.
Using the wrong bulb base type can cause electrical issues.真
Incorrect base types may not fit properly, leading to electrical problems.
What Role Does Wattage Play in Choosing a Bulb?
Choosing the right bulb involves understanding how wattage influences energy consumption and brightness.
Wattage in bulbs determines power consumption and indirectly impacts brightness. Higher wattage usually indicates more brightness but also more energy use, making it crucial to balance efficiency and illumination needs.

Understanding Wattage and Lumens
Wattage measures the amount of energy a bulb uses. Traditionally, higher wattage meant a brighter bulb, but with advancements in lighting technology, this isn’t always the case. Instead, lumens are now used to measure brightness. When selecting bulbs, focus on lumens for brightness and watts for energy consumption.
For example, an LED bulb might use only 10 watts to produce the same brightness as a traditional 60-watt incandescent bulb, which makes it more energy-efficient.
Comparing Wattage Across Bulb Types
Different types of bulbs, such as MR8, MR11, MR16, GU4, GU5.3, and GU10, have varying wattage ratings. Understanding these can help you choose the right bulb for your needs:
| Bulb Type | Typical Wattage Range | Equivalent Incandescent Wattage |
|---|---|---|
| MR8 | 1.8 – 2.5 W | 20 – 25 W |
| MR11 | 3.5 – 5.5 W | 35 – 55 W |
| MR16 | 5 – 10 W | 50 – 100 W |
| GU10 | 5 – 10 W | 50 – 100 W |
Balancing Efficiency and Brightness
When selecting a bulb, consider both your energy efficiency goals and your lighting needs. For areas where you need bright light, such as kitchens or workspaces, you may choose a higher-wattage bulb or one with high lumens. Conversely, for ambient lighting, lower wattage bulbs may suffice.
Also consider other factors such as beam angle3 そして shape4 to ensure the bulb fits your lighting fixture and meets your aesthetic preferences.
Higher wattage always means a brighter bulb.偽
Brightness is measured in lumens, not wattage. High wattage can mean more energy use.
LED bulbs are more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs.真
LEDs use less wattage to produce the same brightness as incandescent bulbs.
How Do Size and Shape Impact Lighting Effectiveness?
Understanding how the size and shape of bulbs affect lighting can transform your space.
The size and shape of a bulb influence its beam angle, light distribution, and compatibility with fixtures. For example, MR16 bulbs, with their multifaceted reflectors, provide focused lighting, making them ideal for spotlights, while GU10 bulbs are often used for broader applications due to their base and shape.

The Role of Size in Lighting
Bulb size determines not only the physical fit5 within a fixture but also affects how light is distributed. Smaller bulbs like the MR8 are compact and often used in tight spaces where precision is essential. These small sizes are particularly effective in accent lighting, drawing attention to specific areas without overwhelming the space.
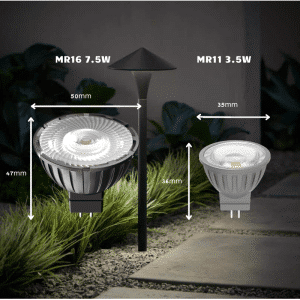
In contrast, larger bulbs such as the MR16 or GU10 provide more extensive coverage due to their size. This makes them suitable for general lighting purposes where a broader beam is needed. The diameter of MR bulbs, indicated by numbers like 8, 11, or 16, relates to eighths of an inch, highlighting the variation in size which influences their application.
Shape’s Influence on Light Distribution
The shape of a bulb can significantly impact the beam angle and focus. MR bulbs, known for their multifaceted reflectors (MR stands for Multifaceted Reflector), concentrate light into a narrow beam. This property makes them ideal for track lighting or recessed downlights where spotlighting is desired.
Conversely, GU bulbs have a broader design that allows for a wider spread of light. The pin base designations (like GU4 or GU5.3) indicate different pin spacing that can affect both the fixture fit and the direction of light emission.
| Bulb Type | 直径 | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| MR8 | 25mm | Accent Lighting |
| MR11 | 35mm | Cabinet Lighting |
| MR16 | 50mm | Spotlights |
| GU10 | 50mm | General Illumination |
Shape and Fixture Compatibility
The bulb’s shape also affects its compatibility with various fixtures. A bulb that doesn’t match the fixture’s design can result in inefficient lighting or even safety hazards. For example, using an MR16 bulb in a fixture designed for broader beam GU10 bulbs might not yield the desired effect.
Understanding these nuances ensures that you select the right bulb type for your specific needs, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics of your lighting setup.
MR16 bulbs did't ideal for general illumination.偽
MR16 bulbs are better for somewhere need safety considerasion like bathroom.
GU10 and MR16 bulbs both provide broader light 真
broader light is because using big beam angle lens for GU10 and MR16.
What Are the Typical Voltage Requirements for These Bulbs?
Voltage requirements vary among MR そして GU bulbs, affecting performance and compatibility.
MR8, MR11, and MR16 bulbs typically require 12 volts, while GU10 bulbs use 120 volts. Understanding these voltage requirements is essential for ensuring bulb compatibility with your fixture and preventing damage.

Understanding Bulb Voltage Requirements
When it comes to lighting, voltage plays a crucial role in determining both the performance and compatibility of a bulb. Let’s break down the voltage needs for each of the popular bulb types: MR8, MR11, MR16, GU4, GU5.3, and GU10.
MR Bulbs
-
MR8, MR11, and MR16 bulbs are designed to work primarily with a low voltage system, typically at 12 volts. This makes them ideal for applications like track lighting and landscape lighting where a transformer is used to step down the voltage.
-
Due to their design, these bulbs provide focused lighting, often used in settings that require precise illumination.
GU Bulbs
-
GU4 そして GU5.3 bulbs also operate at 12 volts, similar to MR bulbs. Their pin base design means they are often found in similar low-voltage applications.
-
In contrast, GU10 bulbs are built for high voltage systems, requiring 120 volts or 230 volts. This makes them suitable for direct connection to the standard household electrical system without the need for a transformer.
| Bulb Type | Voltage Requirement |
|---|---|
| MR8 | 12V |
| MR11 | 12V |
| MR16 | 12V |
| GU10 | 120V / 230V |
Why Voltage Matters?
Choosing the correct voltage is essential for several reasons:
- Compatibility: Ensuring that the bulb matches your fixture’s voltage prevents electrical issues.
- Efficiency: Using the wrong voltage can lead to reduced bulb lifespan and inefficiency.
- Safety: Incorrect voltage usage increases the risk of overheating or damage to your lighting system.
Practical Applications
Understanding these voltage differences can guide you in selecting the right bulb for your needs:
- For outdoor pathways or garden areas, low voltage MR bulbs6 or GU bulbs7 are often preferred due to safety and ease of installation with transformers.
- Indoor settings like kitchens or bathrooms that use recessed lighting might benefit from high-voltage GU10 bulbs for their straightforward installation.
By considering these voltage requirements, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your lighting solutions.
MR16 bulbs require 120 volts for operation.偽
MR16 bulbs typically require 12 volts, not 120 volts.
GU10 bulbs connect directly to household systems.真
GU10 bulbs use 120 volts, suitable for direct connection to home systems.
結論
By understanding these bulb differences, I’ve found that optimal lighting solutions are just a choice away! Choose wisely based on your fixture’s requirements to enhance both functionality and ambiance.
-
Learn detailed specifications and uses of various bulb pin bases.: The most common light bulb base sizes include: · Standard-Medium, a regular sized screw in base: E26 or E27 · Candelabra, a smaller screw in base: E12 … ↩
-
Explore how bulb design affects light distribution and ambiance.: As incandescent light bulbs became commonplace, energy consumption greatly increased and we began to record harmful effects to the climate. Once … ↩
-
Understand how beam angle affects light distribution.: The beam angle measures the light spread from a source, such as a light bulb. Broader beam angles result in more spread-out light, but the light is also less … ↩
-
Discover how shape influences lighting effectiveness.: Remember, the shape of a bulb determines how it shines and disperses its light, and every shape has a usage function: i.e., an intended fixture to be used in! ↩
-
Learn how different bulb sizes influence light spread.: Their design, featuring a reflective surface and a bulged shape, allows for broad and diffused light distribution, making them ideal for track lighting and … ↩
-
Explore how MR bulbs enhance outdoor lighting aesthetics.: This guide will help you to understand the primary differences and best applications for each bulb in a respective setting. ↩
-
Learn why GU bulbs are a top choice for outdoor settings.: Max Efficiency. Very low energy consumption to save you money while reducing carbon emissions. Save up to 50% compared to standard LED bulbs. 50,000 hours … ↩