Introduction
PAR16 and MR16 bulbs may look somewhat similar at first glance, but they have distinct differences that affect their performance and suitable applications. This article aims to clarify these differences.
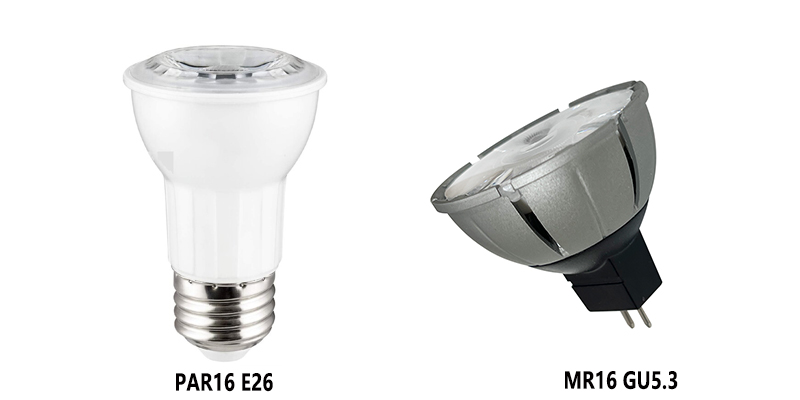

Shape and Design
PAR16 Bulbs
PAR16 bulbs usually have a broader face, allowing for wider light dispersion. They are often used in floodlights or larger track lighting fixtures.
MR16 Bulbs
These bulbs have a smaller face, concentrating the light into a tighter beam. They are ideal for spot lighting and task lighting.
Voltage and Wattage
PAR16 Bulbs
PAR16 bulbs generally run on mains voltage, which is typically 120V in the U.S. or 230V in Europe.
MR16 Bulbs
MR16 bulbs usually operate on low voltage, often 12V, and require a transformer to step down from mains voltage.
Base Type
PAR16 Bulbs
PAR16 bulbs usually come with an E26 or E27 screw base.
MR16 Bulbs
MR16 bulbs typically use a pin base, like GU5.3 or GX5.3.


Light Quality and Color
Both types of bulbs are available in various color temperatures and can offer similar light quality, but the optics in MR16 bulbs may offer better control of light beams.
Energy Efficiency
Both types of bulbs come in energy-efficient LED options, but because MR16 bulbs run on low voltage, they may require a transformer, which can sometimes lead to energy losses.

Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Replace One with the Other?
Given the differences in voltage and base types, a direct replacement usually isn’t possible without modifications.
Conclusion
While PAR16 and MR16 bulbs may serve similar functions, their differences in size, voltage, and base types make them suited for different applications. Knowing these differences can help you choose the right bulb for your needs.