I often wonder about the impact of dimming my LED bulbs on their lifespan. It’s a common choice for many of us seeking energy efficiency and ambiance in our homes. But does frequent dimming really wear them out faster?
Frequent dimming of LED bulbs generally extends their lifespan as it reduces thermal stress. However, factors like the quality of LED drivers and the frequency of on/off cycles also play significant roles in determining longevity.
While it’s reassuring to know that dimming can actually benefit LED bulbs by reducing wear, other aspects such as cycling frequency and driver quality are crucial to consider. Let’s explore these factors in detail to optimize your lighting setup.
Frequent dimming reduces LED bulb lifespan.False
Dimming generally extends LED lifespan by reducing thermal stress.
How Does Thermal Stress Impact LED Lifespan?
Thermal stress is a crucial factor affecting the lifespan of LED bulbs. Understanding how it works can help optimize their performance.
Thermal stress significantly impacts LED lifespan by causing material degradation over time. Managing heat efficiently through quality components and proper design is essential to prolong their longevity.
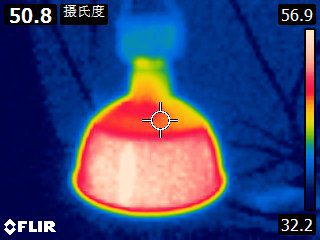
The Basics of Thermal Stress
Thermal stress occurs when there’s a significant change in temperature that affects the physical properties of a material. For LEDs, which are semiconductors, consistent exposure to high temperatures can lead to early failure due to material degradation and reduced efficiency.
LEDs generate heat as a byproduct of light emission. If this heat is not effectively managed, it can accumulate and cause the components to deteriorate. This thermal management1 is crucial for maintaining LED performance over time.
Why Heat is a Major Concern
While LEDs are generally more efficient than traditional bulbs, they are also more sensitive to heat. Excessive thermal stress can lead to issues such as:
- Reduced luminous efficacy (brightness)
- Color shift or changes in light output
- Physical damage to LED components
A table illustrating the relationship between temperature and LED lifespan is shown below:
| LED Tj (°C) | Expected Lifespan (Hours) |
|---|---|
| 75 | 50,000 |
| 85 | 40,000 |
| 95 | 30,000 |
Mitigating Thermal Stress
The key to reducing thermal stress lies in effective heat dissipation strategies:
- Heat Sinks: Use materials with high thermal conductivity to draw heat away from the LED.
- Improved Housing Design: Ensure that the bulb casing allows for adequate airflow to disperse heat.
- Quality Components: Invest in high-quality LED drivers that can handle thermal fluctuations.
By focusing on these aspects, users can significantly extend the lifespan of their LED bulbs.
Real-world Applications and Considerations
In practice, controlling the ambient temperature where LEDs are used can also play a role in reducing thermal stress. For instance, using LEDs2 in a cooler environment or employing additional cooling systems can help maintain optimal operating conditions.
Furthermore, understanding the specific requirements of each LED setup is vital. Customized solutions based on application—whether in residential lighting or industrial settings—can be tailored to manage thermal output efficiently.
Thermal stress causes LED material degradation.True
Thermal stress leads to material degradation, reducing LED lifespan.
LEDs are less sensitive to heat than traditional bulbs.False
LEDs are more sensitive to heat, impacting their performance and lifespan.
What Role Do LED Drivers Play in Longevity?
LED drivers are crucial components affecting the lifespan of LED bulbs, but how exactly do they contribute to longevity?
LED drivers are vital for the longevity of LED bulbs, ensuring stable power supply and minimizing stress on the components.
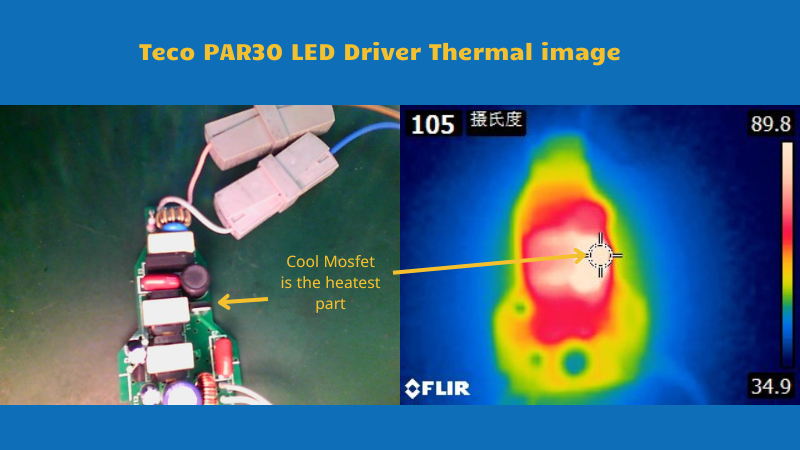
Understanding LED Drivers
LED drivers act as the electrical regulators that manage the power flow to LED bulbs. They convert the high voltage AC current from the power source into a low voltage DC current suitable for LEDs. This conversion process is essential, as LEDs are designed to operate at a specific current level and voltage. Without an efficient driver, LEDs may receive inconsistent power, leading to premature failure.
Importance of Driver Quality
The quality of an LED driver significantly impacts the bulb’s lifespan. High-quality drivers ensure a stable and consistent current, reducing thermal stress on the LEDs. When an LED operates under stable conditions, its components undergo less wear and tear, thereby extending its usable life. Conversely, poor-quality drivers might lead to fluctuations in power supply, increasing the risk of burnout.
Impact on Dimming Performance
Dimmable LED systems rely heavily on the driver’s ability to handle varying levels of current. A good driver accommodates these changes smoothly without causing flicker or noise, both of which can degrade the LED over time. Inadequate drivers might struggle with dimming, causing inconsistent lighting and potentially shortening the LED’s lifespan.
Role in Thermal Management
Drivers also contribute to managing the thermal output of LEDs. Excess heat is a primary factor in reducing LED lifespan. Efficient drivers help dissipate heat effectively, maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing damage to LED components. This thermal regulation is crucial in prolonging the life of the bulb.
Evaluating Different Driver Types
There are various types of LED drivers, including constant current and constant voltage drivers. Constant current drivers are preferred for most applications as they maintain a steady current output regardless of changes in voltage, which is crucial for maintaining longevity. However, the choice between these types depends on specific application needs and compatibility with the LED system.
In summary, choosing high-quality LED drivers3 is paramount for ensuring the longevity of your LED bulbs. They not only provide necessary electrical regulation but also enhance dimming capabilities and thermal management, all of which contribute to extending the life of your lighting systems.
LED drivers convert AC to DC current for LEDs.True
LED drivers convert high voltage AC to low voltage DC suitable for LEDs.
Poor-quality drivers increase LED lifespan.False
Poor-quality drivers cause power fluctuations, reducing LED lifespan.
Are Frequent On/Off Cycles Detrimental to LEDs?
Frequent on/off cycles are common in daily use, but how do they affect the lifespan of LED bulbs?
Frequent on/off cycles can negatively impact LED longevity by causing thermal stress and affecting the drivers. However, high-quality LED drivers can mitigate these effects, ensuring that the bulbs last longer despite frequent cycling.

Understanding Thermal Stress and Its Impact
LEDs generate heat during operation, which can lead to thermal stress4 if the bulbs are switched on and off frequently. This stress results from rapid temperature changes that occur each time the bulb is cycled. While LEDs are generally more resilient to thermal stress compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, excessive cycling can still shorten their lifespan.
For instance, consider a workspace where lights are frequently turned on and off throughout the day. Each cycle subjects the LEDs to a quick change in temperature, potentially leading to microcracks or degradation in the bulb’s components over time. This constant thermal expansion and contraction can wear down the materials used in LEDs, reducing their effective life.
The Role of LED Drivers in Managing Cycles
The LED driver is crucial in regulating power supply to the bulb, ensuring it operates efficiently. High-quality drivers can handle frequent on/off cycles better than lower-quality alternatives.
A robust driver will manage the electrical load smoothly, reducing the strain on the LED components during cycling. In contrast, a subpar driver might allow voltage spikes or drops when the bulb is turned on or off, which can exacerbate wear and tear.
Balancing Energy Efficiency with Longevity
While it’s tempting to turn off lights to save energy, it’s important to balance this with potential impacts on bulb longevity. In environments where frequent cycling is unavoidable, investing in LED bulbs with superior drivers can help mitigate potential damage.
For homeowners or businesses looking to optimize their lighting setup, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Implementing smart lighting systems that gradually adjust brightness rather than abrupt cycling can also be an effective strategy for prolonging LED lifespan.
Frequent cycling shortens LED lifespan due to thermal stress.True
Thermal stress from frequent on/off cycles can degrade LED components.
High-quality LED drivers don't affect bulb longevity during cycles.False
High-quality drivers reduce damage from cycling but can't eliminate it.
Can Dimmed LEDs Save More Energy?
Explore how dimming LED bulbs can lead to significant energy savings.
Dimmed LEDs consume less power by reducing their light output, leading to substantial energy savings. This simple yet effective method not only lowers electricity bills but also contributes to a sustainable environment. However, the exact savings depend on several factors, including the type of LED and its usage patterns.

Understanding LED Dimming
When you dim an LED bulb, you essentially reduce the power it consumes. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which waste a lot of energy as heat, LEDs are designed to be more efficient. When dimmed, LEDs decrease their light output by lowering the current flowing through them. This results in less energy consumption and subsequently lower electricity bills.
The Mechanics Behind Energy Savings
To truly grasp how dimming saves energy, consider the basic principle: power consumption is directly proportional to light output. For instance, if you dim your LED to 50% of its maximum brightness, it typically uses about 50% of the energy compared to when it is fully lit. This linear relationship is key to understanding how dimming can lead to energy efficiency.
| Brightness Level | Energy Consumption |
|---|---|
| 100% | 100% |
| 75% | 75% |
| 50% | 50% |
| 25% | 25% |
Factors Influencing Energy Savings
However, not all LEDs are created equal. The quality of the LED driver significantly affects energy savings. High-quality drivers ensure that the bulb dims smoothly without flickering or losing efficiency. Additionally, the environment in which the LED is used also plays a role. For example, dimming lights in areas that don’t require full brightness, such as hallways or during nighttime, maximizes savings.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Dimming LEDs contributes not only to economic savings but also environmental benefits. Reduced energy consumption lowers carbon footprints and supports sustainable energy practices. Households and businesses can significantly cut their electricity expenses by integrating dimmable LEDs into their lighting systems.
Ultimately, while dimming provides immediate benefits in terms of reduced power consumption and costs, it’s essential to consider the quality and suitability of the LED for your specific needs to fully capitalize on these advantages. To explore more about these benefits, check out our section on The Role of LED Drivers5 in ensuring efficiency and longevity.
Dimming LEDs to 50% saves 50% energy.True
LEDs consume less power when dimmed, directly reducing energy use.
All LED drivers ensure smooth dimming.False
Only high-quality drivers provide efficient, flicker-free dimming.
Conclusion
By understanding how dimming impacts LED lifespan, I can make smarter choices about my lighting that not only enhance my home environment but also save energy.
-
Explore techniques for optimizing LED performance through effective heat management.: The first solution may be to select an enclosure with a material composition rated for high thermal conductivity. If enough heat can escape though the enclosure … ↩
-
Learn how environmental control can extend LED bulb lifespan.: However, LED lights are designed to work much better in colder temperatures compared to traditional lighting. You can use these luminaires in cold storage … ↩
-
Learn how to select efficient LED drivers for better bulb longevity.: It is important to know your LED’s specs so you know the recommended drive currents and heat sink requirements so you don’t burn the LED out … ↩
-
Learn how thermal stress affects LED longevity and how to minimize it.: Inefficient drivers generate extra heat, compounding overall thermal stress on LED components and potentially reducing the device’s lifespan. ↩
-
Discover how LED drivers enhance energy savings and bulb longevity.: LED drivers’ ability to deliver precise power to LEDs significantly reduces energy consumption compared to traditional lighting technologies. LEDs consume up to … ↩