Transformers are essential components in electronics, playing a pivotal role in the functioning of numerous devices. This blog will teach you how electronic transformers can be used in lighting and other fields.
Introduction
Often regarded as the backbone of electrical systems, transformers are vital in converting voltages to desired levels, ensuring electronic devices’ safe and efficient operation. But what exactly are transformers, and how do they work? This comprehensive guide will delve into the fundamentals of electronic transformers, shedding light on their diverse applications and importance.
What is a Transformer?
A transformer is a static electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers are used to increase (step-up) or decrease (step-down) voltage levels, ensuring that electronic devices receive the appropriate voltage for optimal operation.
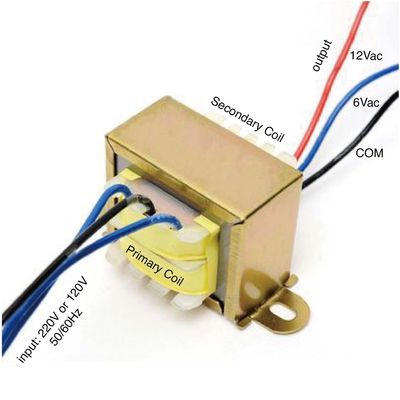
Key Components of a Transformer
- Primary Coil: The coil that receives the input voltage.
- Secondary Coil: The coil that delivers the output voltage.
- Core: The magnetic core that facilitates energy transfer between the primary and secondary coils.
How Does a Transformer Work?
The operation of a transformer is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, it creates a varying magnetic field around it. This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary coil, thus transferring energy from the primary to the secondary circuit. The voltage induced in the secondary coil depends on the ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil.
Types of Transformers
Transformers come in various types, each designed for specific applications. Let’s explore some common types:
- Power Transformers: Used in transmission networks to step-up or step-down voltage levels.
- Distribution Transformers: Found in distribution networks to provide the final voltage transformation.
- Isolation Transformers: Used to isolate different sections of electrical systems for safety.
- Electronics Transformers: Specifically designed for electronic devices, ensuring they receive the correct voltage.
Focus on Electronics Transformers
Electronics transformers, often referred to as electronic voltage transformers, are crucial in the realm of consumer electronics. These transformers are typically smaller and more efficient, designed to handle low power levels and provide stable voltage to sensitive electronic components.

Applications of Electronics Transformers
Electronics transformers are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Power Supplies: Ensuring that electronic devices receive the correct operating voltage.
- MR16 Lighting: Low-voltage halogen lamps are often used in residential and commercial lighting.
- Dimmable Lighting: Allowing users to adjust light intensity by controlling the voltage supplied to the lamp.
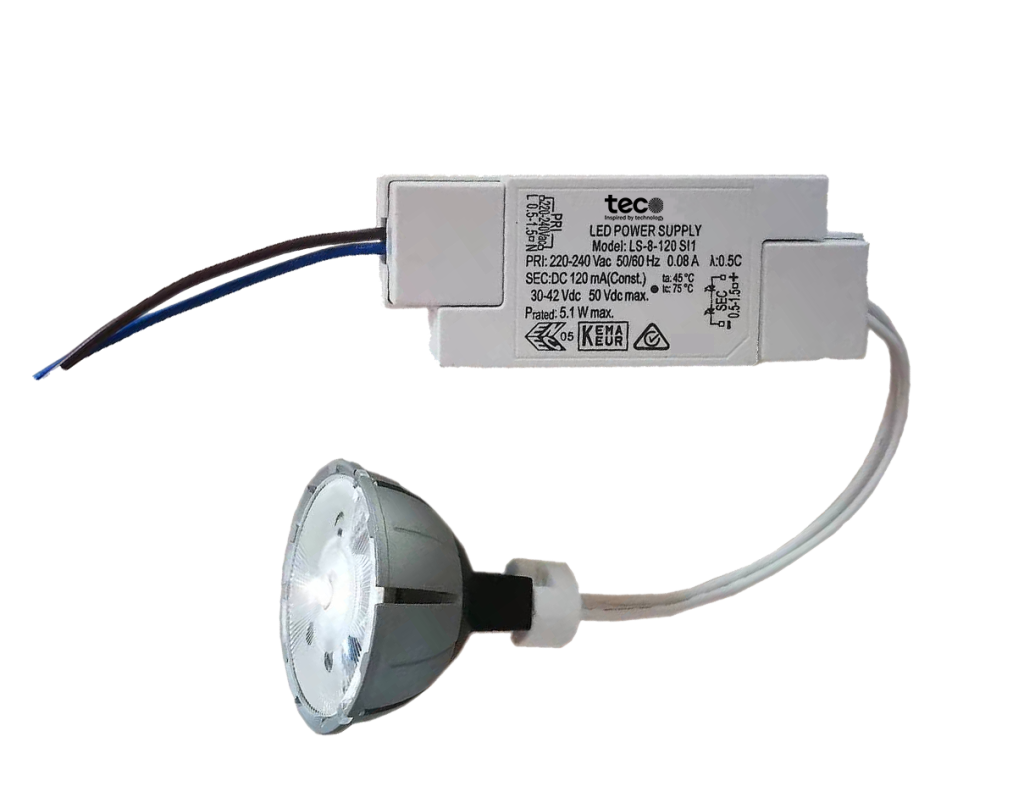
MR16 Transformers
The MR16 lamp is a popular type of halogen or LED lamp used for track lighting, recessed ceiling lights, and landscape lighting. These lamps operate at low voltages, typically 12V, requiring a transformer to step down the mains voltage to the appropriate level. MR16 transformers are designed to provide stable voltage, ensuring the longevity and consistent performance of these lamps.
Dimmable Transformers
Dimmable transformers add an extra layer of functionality, allowing users to adjust the brightness of their MR16 lamps. These transformers are compatible with dimmer switches, providing smooth and flicker-free dimming capabilities.

Importance of Transformers in Electronics
Transformers play a critical role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electronic devices. They provide:
- Voltage Regulation: Ensuring devices receive the correct voltage, preventing damage and enhancing performance.
- Isolation: Protecting sensitive electronic components from electrical surges and interference.
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy losses, contributing to the overall efficiency of electronic systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While transformers are indispensable in electronics, they come with their own set of challenges:
- Heat Dissipation: Transformers generate heat, which must be managed to prevent overheating and ensure longevity.
- Efficiency: Striking a balance between size, weight, and efficiency is crucial, especially for portable electronic devices.
- Compatibility: Ensuring transformers are compatible with various electronic components and standards is vital for seamless integration.
Conclusion
Transformers are the unsung heroes of electronic systems, providing the necessary voltage regulation and isolation to ensure the smooth operation of countless devices. From MR16 lighting to dimmable systems, transformers are integral to the functionality and efficiency of modern electronics. Understanding their basics, functions, and applications can help us appreciate the complexity and importance of these essential components.
In summary, transformers in electronics are not just about stepping up or stepping down voltages; they’re about enabling the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of the myriad of devices that power our daily lives. So, the next time you flip a switch or power up a device, take a moment to appreciate the humble transformer working tirelessly behind the scenes.






