Introduction:
LED spotlights are better than halogen bulbs! This article explores the differences between these two popular lighting options, providing you with a comprehensive analysis based on energy efficiency, manufacturing processes, cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and more. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of how to choose the right LED spotlight lighting for your needs.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
LED Spotlights
- Energy Efficiency: LED (Light Emitting Diode) spotlights stand out for their exceptional energy efficiency. On average, an LED bulb consumes about 7 watts of power to produce the same amount of light as a 60-watt halogen bulb. This translates to a 75% reduction in energy usage, which not only conserves energy but also significantly reduces electricity bills.
- Working Principle: LEDs are made using semiconductor materials that emit light when an electric current passes through them. This technology, known as electroluminescence, involves key materials like silicon and gallium, which efficiently convert electrical energy into light.
- Heat Management: LED spotlights include efficient heat management systems, often using aluminum alloy and ceramic materials to conduct and dissipate heat.
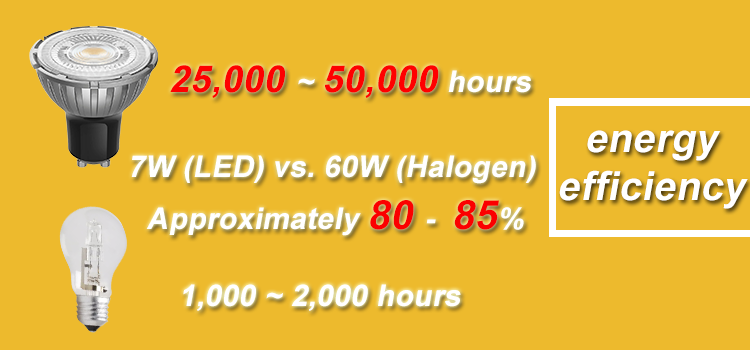
- Power Comparison: 7W (LED) vs. 60W (Halogen).
- Energy Consumption Reduction: Approximately 80-85%.
- Lifespan: LED spotlights typically last between 25,000 to 50,000 hours, whereas halogen bulbs last only 1,000 to 2,000 hours.
Halogen Bulbs
- Energy Efficiency: Halogen bulbs are less efficient than LEDs. They operate similarly to incandescent bulbs, generating a significant amount of heat, which is a byproduct of their design. This heat loss represents wasted energy, making halogen bulbs less ideal for energy savings.
- Working Principle: Halogen bulbs are an improved version of incandescent bulbs, where halogen gas surrounds the filament. This gas reacts with evaporated tungsten, preventing blackening of the bulb and extending its life.
- Materials: Made primarily from glass, tungsten filaments, and a small amount of halogen gas (like iodine or bromine).
- Heat Effect: Halogen bulbs generate a lot of heat because they produce light by heating the filament to very high temperatures.
- Heat Emission: High (a significant portion of energy is converted to heat rather than light).
Environmental Impact

LED Spotlights
- Carbon Footprint: Reduced due to lower energy consumption.
- Resource Conservation: Extended lifespan minimizes resources needed for manufacturing, packaging, and transportation.
- Waste Reduction: Longer lifespan leads to less frequent replacements and less waste in landfills.
Halogen Bulbs
- Shorter Lifespan: Frequent replacements contribute to increased waste.
- Resource Usage: Higher energy consumption and shorter lifespan increase environmental impact.
Manufacturing Processes
LED Spotlights
- Production Process: Involves complex semiconductor manufacturing techniques, including photolithography, etching, doping, and deposition of multiple semiconductor layers. These processes require high-precision equipment but relatively low energy consumption and produce minimal harmful waste.
Halogen Bulbs
- Production Process: Similar to traditional incandescent bulbs, involving glass blowing and filament manufacturing. This process is energy-intensive, especially during tungsten filament production, which requires significant electricity to heat the tungsten to high temperatures.
Working Principles and Energy Efficiency
LED Spotlights
- Working Principle: LEDs produce light through electroluminescence, where electrical energy is efficiently converted into light with minimal heat generation.
- Energy Efficiency: Typically, 150-200 lumens per watt, far superior to halogen bulbs’ 15-24 lumens per watt.
Halogen Bulbs
- Working Principle: Halogen bulbs emit light by heating the filament to incandescence, resulting in low light efficiency and high heat production.
- Energy Efficiency: Lower, as they require more energy to maintain the high temperatures needed for the filament to glow.
Cost-Effectiveness
Initial Cost and Long-Term Savings
- LED Spotlights: Higher initial cost but quickly offset by lower operating costs. An average LED spotlight can save about $6 per year in energy costs, depending on usage.
- Halogen Bulbs: Lower initial cost but higher operating costs due to frequent replacements and higher energy consumption.
Cost Analysis

- LED Spotlights: Approximately $5 per spotlight.
- Halogen Bulbs: Approximately $3 per bulb.
- Energy Savings: LEDs can save about $6 per spotlight per year.
- Replacement Costs: LEDs have a much longer lifespan, reducing the frequency and cost of replacements.
Heat Dissipation and Safety
LED Spotlights
- Heat Dissipation: LEDs generate relatively low heat due to high energy conversion efficiency. They use aluminum-based heat sinks to dissipate heat, maintaining optimal performance and longevity.
- Safety Features: LEDs’ low operating temperature reduces the risk of burns and fire hazards. They also operate on low-voltage DC power, minimizing electrical hazards.
Halogen Bulbs
- Heat Dissipation: Halogen bulbs generate significant heat, with filament temperatures reaching 2500°C to 3000°C and outer bulb temperatures around 500°C. Proper ventilation is necessary to avoid heat buildup.
- Safety Features: High operating temperatures increase the risk of burns and fire hazards. High-quality halogen bulbs use explosion-proof designs to contain glass shards if the bulb breaks.
Light Quality and Versatility
LED Spotlights
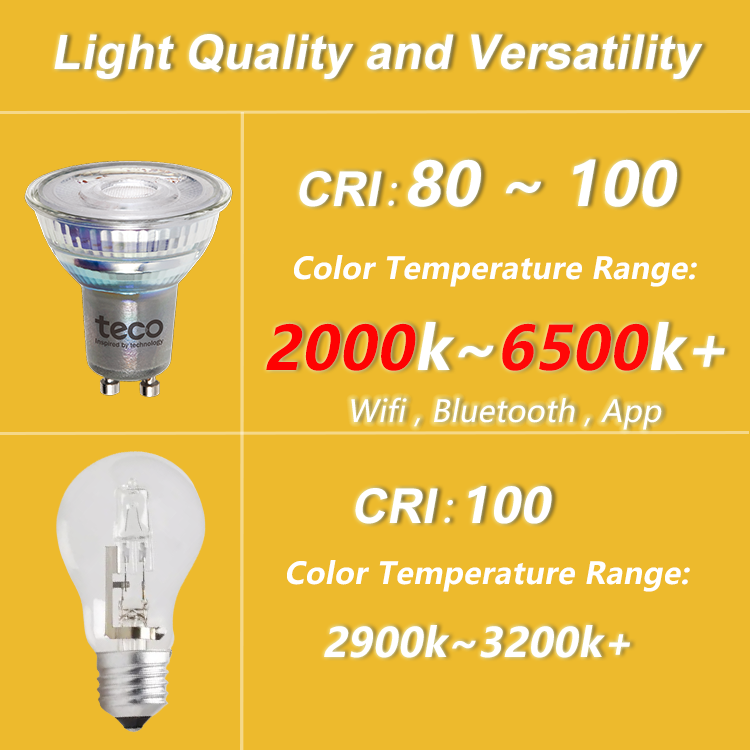
- Color Rendering Index (CRI): Typically 80 to 90, with some achieving up to 100 through advanced techniques.
- Color Temperature Range: From very warm (2000K) to very cool (6500K), offering flexibility for different applications.
- Smart Control: Advanced smart control options via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, apps, and program controllers, providing unprecedented flexibility and convenience.
Halogen Bulbs
- Color Rendering Index (CRI): Approximately 100, providing excellent color accuracy.
- Color Temperature: Generally between 2900K to 3200K, ideal for warm, relaxing environments.
- Dimmer Compatibility: Excellent dimming performance, with smooth transitions and warmer light when dimmed.
Conclusion
Choosing between LED spotlights and halogen bulbs requires considering various factors, including efficiency, cost, safety, and specific lighting needs. LED spotlights offer superior efficiency, longevity, and environmental benefits, making them an excellent choice for those seeking a blend of performance and sustainability. As costs continue to decrease and technology advances, LED spotlights not only become a practical choice but also an investment in energy savings and environmental responsibility. This detailed analysis aims to guide you in understanding the complex dynamics between these two popular lighting technologies, ensuring you make an informed decision that aligns with your current needs and long-term environmental goals.